Export Lovable.dev to React: Step-by-Step Guide


Migrating Lovable.dev code into a production-ready React application requires careful planning and technical expertise. The process involves several critical considerations that can impact your project’s success. In this guide, we’ll show how to export Lovable.dev to React and prepare the code for production.
While CLI migration might seem straightforward, the reality is more complex. The migration process demands deep understanding of both platforms to ensure nothing breaks during transition. Technical challenges often arise that require experienced problem-solving skills.
SEO considerations make React a strategic choice, but implementation isn’t simple. Next.js offers crucial advantages for search rankings, but proper configuration is essential. While Vite builds are quick without SSR, search engine crawlers require Server-Side Rendering for proper content indexing – a technical hurdle that needs expert handling.
This comprehensive guide examines the intricacies of code migration. We’ll explore various export methods, address common migration challenges, and discuss React environment setup requirements. While AI coding agents can assist, successful migration typically requires human expertise to navigate complex scenarios.
Converting a prototype into production-ready code requires technical precision and experience — and if you want a safer path from prototype to real product, this is the exact scope of Lovable Prototype Upgrade.
What You Get When Exporting from Lovable.devThe Lovable.dev to React export process yields a complete codebase, but managing this transition effectively requires technical expertise. Understanding what’s included – and what isn’t – is crucial for planning your migration strategy.
Overview of exported codebase
The export package provides a Vite-based React application that maintains UI components and client-side logic. This preserves your user flows and interfaces, but requires careful handling during migration.
The project structure follows React conventions with specific directories:
- /components
- /pages or /app
- /styles
- /lib
- /api
This organization demands thorough understanding for effective scaling and maintenance. While screen components map to UI elements and routes are defined, proper implementation requires technical expertise.
The export includes Supabase/Postgres database schemas in the supabase/migrations directory. Creating a new database instance requires careful attention to maintain data integrity.
Limitations of the export
The export provides frontend components, but crucial elements like authentication, Stripe integration, and AI orchestration features remain with Lovable’s managed services. This architectural decision maintains platform flexibility but introduces significant technical challenges requiring specialized knowledge.
The backend infrastructure requires separate reconstruction from scratch. While Lovable specializes in generating frontend code that can be exported to preferred frameworks like Next.js or custom React implementations, transitioning to a production-ready tech stack demands significant technical expertise and resources.
For security purposes, the export package intentionally excludes sensitive configuration data. API keys and secrets are not included in the export to maintain data protection, necessitating manual configuration post-export by experienced developers.
Several critical limitations require attention:
- Implementation of secure authentication flows and role-based access control systems may be incomplete or missing
- Encrypted data handling mechanisms need complete reconstruction
- Applications involving user accounts, payment processing, or sensitive data typically require substantial architectural modifications
Ensure these critical steps are completed by qualified personnel before proceeding with export:
- Document all integrations – Capture screenshots of ‘Settings → Integrations’ and catalog all third-party services powering authentication, payments, and AI functionalities
- Note configuration details – Document all API keys, callback URLs, and webhook endpoints requiring reconfiguration
- Save environment variables – Create comprehensive documentation of environment variables excluded from export
- Verify project builds successfully – Ensure proper compilation within Lovable before export
- Review permissions – Verify export authorization for team projects
- Think about version control – Select between immediate ZIP download or Git/GitHub integration for version tracking
The local development environment setup requires careful consideration and technical expertise. Essential requirements include Node.js installation, npm package management, a professional-grade code editor such as Visual Studio Code, and command-line proficiency for executing complex installation commands.
A thorough technical assessment of the export package and meticulous preparation by experienced developers is crucial to navigate potential migration complexities, especially if this export is being treated as an MVP, where scope discipline matters (see How to Build an MVP for a SaaS Startup).
The transition to React development demands specialized knowledge. The exported codebase requires expert handling to integrate effectively with existing CI/CD pipelines and established development workflows.
Read Related
Lovable.dev provides two export options: GitHub integration and manual ZIP download. Each method presents distinct technical challenges and implications for ongoing development.
Benefits of GitHub Integration
GitHub integration, while technically complex, offers advanced version control capabilities]. It establishes a sophisticated pipeline between your project and a GitHub repository.
Key technical considerations include:
- Automated synchronization: Complex state management between Lovable and GitHub repository, requiring careful monitoring.
- Version control: Advanced Git functionality demanding thorough understanding of branching strategies.
- Deployment integration: Technical configuration requirements for Vercel or Netlify connections.
- Team workflows: Complex permission structures and code review protocols.
- Development environment: IDE setup and synchronization challenges across distributed teams.
The GitHub integration establishes a bidirectional synchronization system, requiring careful management of merge conflicts and state reconciliation.
When to use manual ZIP download
The ZIP download option provides immediate access to the project files. However, this approach requires careful consideration of several technical complexities:
- Quick access: Immediate code retrieval without setup procedures, though proper configuration requires technical expertise.
- No GitHub needed: Suitable for environments without GitHub integration, but limits collaborative development capabilities.
- Fast backups: Enables snapshot creation, though proper backup strategy implementation demands systematic planning.
- One-time exports: Suitable for isolated deployments, but requires careful consideration of future maintenance needs.
- Non-technical sharing: While ZIP files are accessible, proper code distribution requires structured documentation.
ZIP downloads, though seemingly straightforward, present significant technical challenges regarding version control implementation and synchronization management.
How to avoid sync issues
Version control and synchronization present complex technical challenges. Consider these critical factors:
For GitHub integration:
- Keep repository paths stable: Repository path modifications can severely disrupt synchronization processes, requiring expert intervention.
- Know how two-way sync works: Bidirectional synchronization demands sophisticated state management expertise.
- Handle disconnects properly: Integration interruptions require careful management of code states and repository relationships.
For manual downloads:
- Start Git right away: Initial version control setup requires precise command execution:
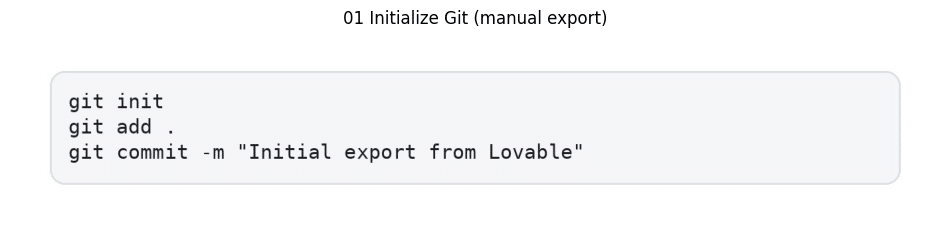
- Push to remote repository: Remote repository configuration demands careful attention:
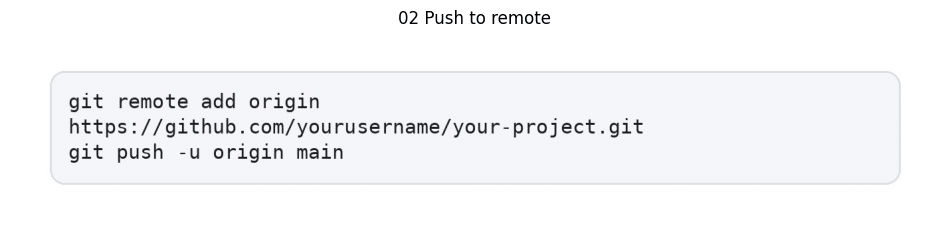
- Handle large files with caution: Implementing Git LFS for files exceeding GitHub’s 100MB limit requires specialized configuration and expertise.
Manual downloads, while appearing convenient for rapid development, often lead to critical version control challenges. When AI agents introduce breaking changes weeks later, the absence of proper version history can create significant technical complications — this is one of the classic MVP failure patterns described in Minimum Viable Product (MVP): 7 Common Mistakes to Avoid.
GitHub integration implementation requires careful consideration based on project complexity. While manual ZIP downloads might suffice for prototype testing or static archived projects, collaborative development demands robust version control infrastructure.
Step-by-Step: GitHub Export ConfigurationThe GitHub export process requires careful attention to technical details. This complex procedure establishes the foundation for professional development workflows, enabling code management across multiple development environments.
GitHub Integration Setup
The GitHub integration process involves several critical configuration steps:
- Access the project through Lovable’s development interface
- Locate the GitHub integration icon in the navigation panel (alternatively, navigate to Settings followed by Integrations or Connectors)
- Initiate GitHub connection through the dedicated interface
- Process GitHub’s authorization protocol via new browser session
- Configure appropriate GitHub account or organizational access
- Review and authorize required permissions for repository management
The integration process requires precise configuration. This establishes the technical framework for code migration procedures.
Repository Configuration
Post-connection repository setup involves multiple technical considerations:
- System initializes main branch with specific configurations
- Platform establishes bidirectional synchronization protocols
- Repository state maintains consistency with Lovable-side modifications
The synchronization mechanism requires careful monitoring. Repository management becomes increasingly complex as team size grows, necessitating experienced oversight of GitHub workflows.
The platform supports advanced branching strategies through the configuration interface. This functionality enables sophisticated source code migration implementations for feature testing.
Local Development Setup
Local environment configuration requires precise execution:
- Access repository URL through Lovable’s GitHub configuration interface (format: https://github.com/yourusername/repository-name.git)
- Navigate to GitHub’s repository interface and locate the Code section
- Extract repository URL for local configuration
- Initialize local development environment via terminal interface
- Execute: git clone https://github.com/yourusername/repository-name.git
- Navigate to project directory: cd repository-name
- Install required packages: npm install
- Launch development environment: npm run dev
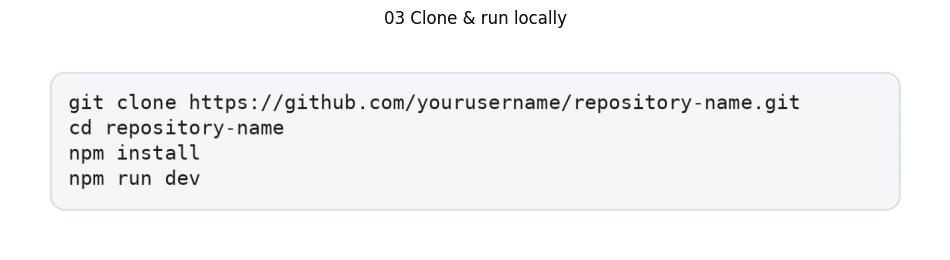
The local project setup requires careful technical consideration. While this enables IDE integration for React migration, the complexity of development environments like VS Code or Cursor with AI capabilities demands thorough understanding of GitHub and Lovable synchronization protocols.
For repository reset procedures:
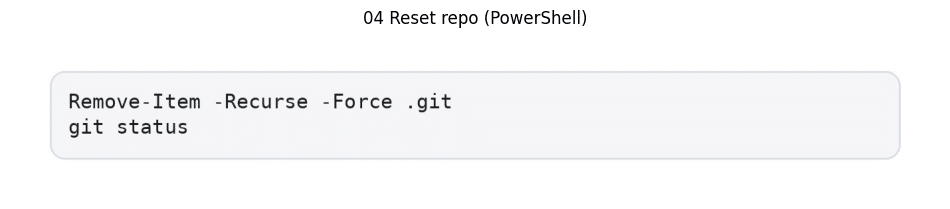
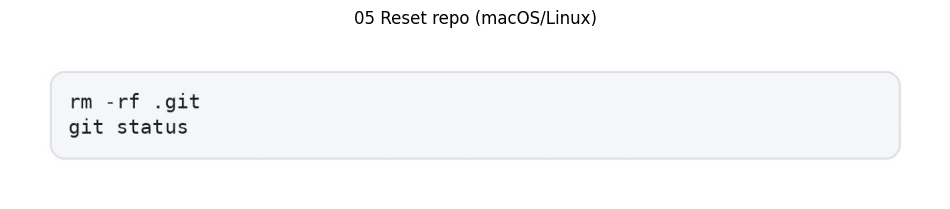
This reset procedure requires careful implementation when migrating code to new repositories or initializing clean version control states.
Post-GitHub integration, some developers continue Lovable-based development. Technical considerations include temporary preview interruptions following initial GitHub connection. Preview restoration typically requires new commit implementation and interface refresh.
Development workflow optimization often involves multi-environment strategies. This includes code modifications through professional IDEs, localhost validation, GitHub version control, and Lovable synchronization. This complex approach maintains version control integrity during the critical NoCode to React transition phase.
Post-Export Technical ConsiderationsExported React implementations from Lovable frequently encounter technical complexities requiring resolution. These post-export challenges impact approximately 80% of migrated projects according to technical analysis. Professional code migration expertise significantly reduces resolution timeframes.
Environment Variable Configuration
Initial export failures commonly stem from environment variable absence. Lovable’s security protocols exclude API credentials and sensitive configurations from exported codebases, requiring manual configuration for external service connectivity.
Implementation procedure:
Implementation procedure:
- Generate .env.local file in root directory
- Configure required environment variables:
- Implement server restart protocol.
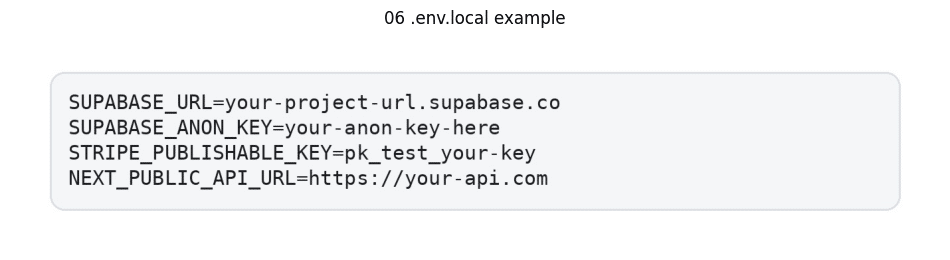
Local environment variable implementation often presents significant challenges post-export. Missing environment configurations frequently result in silent API failures or complex error messages. Security best practices dictate excluding .env.local from version control – immediate .gitignore configuration is essential.
Outdated or broken dependencies
Dependency version conflicts represent a critical challenge in the React migration process. Error manifestations typically appear as:
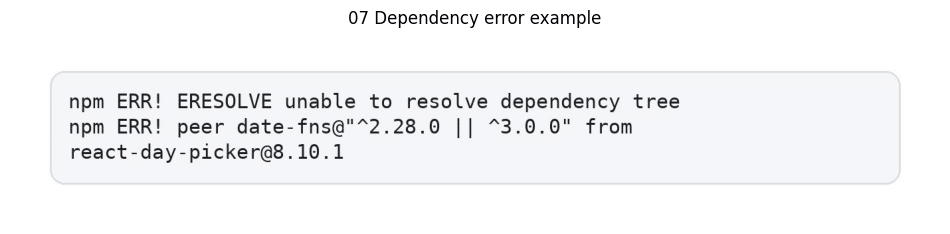
These issues emerge when exported code references non-existent or incompatible dependency versions. For instance, projects might reference unavailable versions like date-fns@4.1.0.
Resolving dependency conflicts requires systematic intervention:
- Examine package.json for problematic version specifications
- Update incompatible versions to supported releases (e.g., modify “date-fns”: “^4.1.0” to “date-fns”: “^2.30.0”)
- Execute comprehensive installation reset:
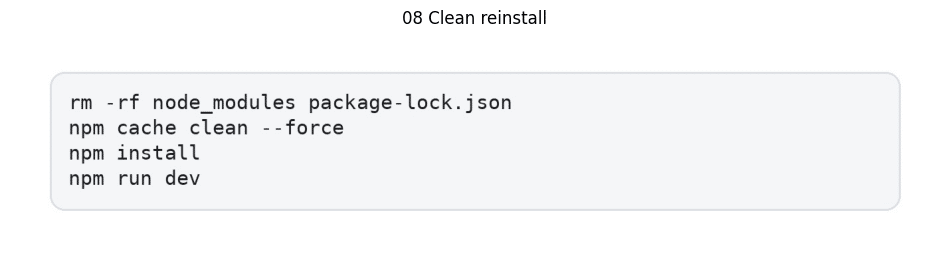
Post-cloning security vulnerability assessment through npm audit fix is crucial, particularly for meeting CI pipeline requirements in deployment phases.
Preserve helper and glue code
A critical consideration post source code migration involves retaining essential infrastructure code. Lovable generates sophisticated helper functions and API route wrappers that establish frontend-backend connectivity. This infrastructure, while appearing superfluous, is fundamental to application functionality.
Removing infrastructure code results in multiple failure points:
- 404 responses from fetch operations
- Authentication persistence failures
- Non-functional form submissions
- Incomplete database operations
Comprehensive flow validation is essential before code modification. Manual testing of critical pathways including signup, login, and checkout functionalities is mandatory. Documentation through code comments proves more effective than removal until full functionality understanding is achieved.
Starting new feature development before validating the local environment setup often leads to complex, misleading bugs that obscure the original issue. A methodical approach demands establishing a fully functional exported application before initiating feature enhancements.
These three critical challenges – environment configurations, dependency management, and infrastructure code maintenance – make the NoCode to React transition particularly complex. While the migration process requires specialized expertise, the end result delivers a fully customizable React application with complete control over the codebase.
Set Up Your React EnvironmentThe React environment configuration following a Lovable export demands meticulous attention. This crucial phase requires technical proficiency to establish connectivity between exported code and development infrastructure.
Install dependencies and run dev server
Post-repository clone or export file extraction, dependency installation requires specific package management expertise:
- Navigate to the project directory via terminal
- Identify the appropriate package manager through lock file analysis:

Initialize the development server post-installation:
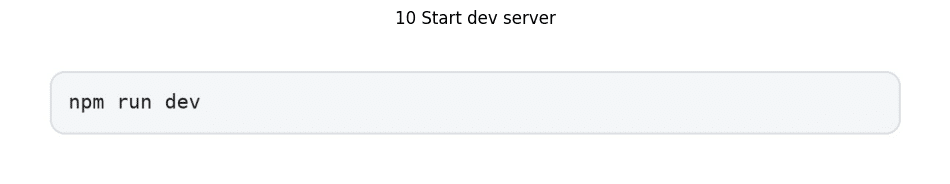
The application should initialize at http://localhost:3000. Access requires following the localhost link displayed in the terminal.
Setup complexity varies with project scale, potentially extending beyond the typical 5-minute timeframe for larger applications.
Configure .env.local and secrets
Proper environment variable configuration is critical. Security protocols exclude sensitive information from exports:
- Locate the .env.example file in project root
- Create .env.local in identical location
- Migrate variables from .env.example to .env.local
- Configure valid API keys and credentials
Example .env.local structure:

Manual API key and secret configuration is mandatory as Lovable excludes these from exports.
Verify all user flows work
Comprehensive testing is essential for validating setup integrity:
- Application initialization without errors
- Database connection verification
- Authentication system validation
- Storage operation confirmation.
Testing major user flows requires specialized expertise to identify potential issues early. Developers often underestimate the complexity of validating local setups before implementing new features.
Technical challenges frequently arise from these critical areas:
- Environment variable misconfigurations (the primary source of system failures)
- Unresolved dependency vulnerabilities requiring npm audit fix
- Incomplete integration code between components
For Supabase connectivity issues, proper configuration of the .env.local file with accurate project identifiers, URLs, and authentication keys is essential.
Projects implementing Stripe, OpenAI, or authentication services demand precise key matching with the original Lovable project specifications.
A correctly configured environment that mirrors your Lovable project requires technical proficiency. This foundation is crucial for feature development, code refactoring, and production deployment preparation. The code migration process demands specialized knowledge and expertise.
Integrate AI Coding Agents for Faster DevelopmentAI coding agents present complex challenges in optimizing React development post-Lovable migration. These sophisticated tools require careful implementation as development assistants that analyze codebases, propose modifications, and generate features based on natural language inputs.
Choose between Cursor, Claude, or Windsurf
Each AI coding assistant presents unique technical complexities:
Cursor operates as a VS Code fork with integrated AI capabilities. The platform implements advanced codebase indexing for comprehensive repository analysis. Its Composer mode handles intricate refactoring tasks across multiple files. Technical requirements include:
- Multi-file project analysis capabilities
- Coordinated AI agent operations
- Extended context processing for comprehensive code analysis
Windsurf (formerly Codeium) implements a streamlined interface compared to Cursor. Its default agent mode automatically retrieves relevant code without manual context selection. The platform’s “agentic first” approach requires:
- Automated code indexing and retrieval
- Command execution without manual intervention
- Requires expert knowledge for proper file structure implementation
Claude Code employs a sophisticated command-line interface that demands technical expertise beyond basic coding skills. Its complex natural language processing capabilities often necessitate precise clarification exchanges before executing commands.
Provide context to the agent
The complexity of AI assistant implementation requires careful consideration of context delivery:
- Curate minimal tools – Implementing AI tools demands strategic selection to avoid functional overlap, similar to maintaining clean architecture in complex codebases
- Supply canonical examples – Technical implementation requires carefully selected representative cases rather than exhaustive edge case documentation
- Enable progressive disclosure – Proper configuration allows AI agents to discover context through systematic exploration rather than bulk information transfer
The “Chat mode” implementation requires technical expertise to effectively evaluate approaches before modifying production code. This complex interaction process demands understanding of architectural trade-offs and technical implications.
Use AI to build features and refactor
Post-migration development workflows present significant technical challenges:
For debugging challenges:
- Complex component-level error analysis
- Advanced diagnostic processes requiring chain-of-thought reasoning
- Systematic issue investigation protocols
For feature development:
- Technical concept validation in Chat mode
- Comprehensive architecture and interface planning
- Critical evaluation of implementation alternatives
Implementing AI tools in React migration requires specialized expertise. While tools like Lovable can assist with UI prototyping, and Cursor/Windsurf help with debugging and business logic integration through GitHub, the process demands deep technical knowledge to leverage each tool effectively.
Though Windsurf and Cursor demonstrate prowess in code generation, they often struggle with intricate visual implementations. While tools like Fusion offer visual editing capabilities for AI-generated components, proper integration requires substantial expertise.
It’s crucial to understand that AI coding assistants function optimally under professional supervision rather than autonomously. While they can accelerate prototyping and MVP development, production applications demand expert oversight, particularly regarding security protocols and performance optimization.
Avoid the Rewrite TrapThe post-export phase presents a critical decision point: whether to refactor existing code or initiate a complete rebuild. This decision requires careful technical evaluation to avoid the “rewrite trap” – an expensive pitfall of unnecessarily rebuilding functional applications.
Why you shouldn’t rebuild working systems
Complete system rebuilds often result in significant productivity losses and team frustration [3]. Despite the allure of starting fresh, this approach introduces substantial risks:
- Loss of meticulously developed functional features
- Extended development cycles without new functionality
- Introduction of regression issues
- Redundant problem-solving efforts
The “Strangler Pattern” presents a more strategic approach, enabling gradual system replacement while maintaining operational stability. This pattern allows concurrent operation of existing frameworks with React during component migration.
Successful migration hinges on three critical factors: technical feasibility assessment, resource allocation strategy, and comprehensive risk management. Without expert planning, projects often encounter scope expansion and timeline extensions that could be prevented with proper technical oversight.
Focus on feature delivery
Maintaining consistent feature releases during code migration presents significant challenges. While breaking work into smaller units theoretically enables gradual deployment, the technical complexity often requires expert oversight to prevent system disruptions.
Post-React migration, the temptation to rewrite functional code should be approached with caution. Each modification requires thorough evaluation of user impact versus technical improvements, a balance best struck by experienced teams.
Critical considerations for NoCode to React transitions include:
- Identifying isolated features suitable for migration (authentication systems, payment flows)
- Implementing robust versioning and deployment protocols
- Conducting thorough production testing before wider rollout
- Maintaining legacy systems until new implementations prove stable
This methodical approach requires specialized expertise to minimize risks while maintaining market presence. System stability demands careful orchestration throughout the transition.
Refactor only when necessary
Strategic refactoring demands deep technical knowledge to improve functionality while preserving behavior. Key objectives include:
- Optimizing performance through redundancy elimination
- Enhancing maintainability for future modifications
- Implementing cleaner architecture to prevent conflicts
Post-legacy code migration refactoring should be selective, focusing on:
- Critical performance bottlenecks affecting user experience
- Unsustainable maintenance overhead
- Technical limitations blocking essential features
- Security vulnerabilities requiring immediate attention
AI-assisted coding introduces complex interdependencies – resolving one issue may trigger others. This necessitates experienced oversight for incremental improvements.
Lovable’s rollback strategy requires careful implementation – reverting changes demands technical expertise to prevent cascading issues. Professional assessment often reveals when alternative approaches surpass problematic solutions.
Your code migration platform journey requires expert guidance to navigate complete rewrites, maintain feature delivery, and implement purposeful refactoring.
Deploy and Maintain Your React AppTransitioning your React application to production requires careful consideration of hosting infrastructure and monitoring strategies. The complexity of deployment often necessitates specialized expertise to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Use Vercel, Netlify, or custom hosting
While Vercel offers sophisticated infrastructure with impressive metrics like 22-60ms Time To First Byte (TTFB) and cold start elimination through Fluid Compute technology, configuring these features demands technical proficiency. Their Hobby tier provides substantial resources – 100GB bandwidth, 100 hours of build execution, and 1 million function invocations monthly.
Netlify’s advanced features require careful implementation:
- Form handling integration complexities
- Identity authentication setup challenges
- A/B testing configuration requirements
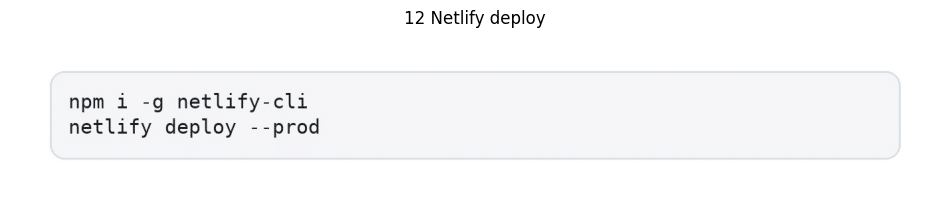
Netlify deployment involves intricate steps:
- CLI installation via npm i -g netlify-cli
- Production deployment using netlify deploy –prod
- UI-based deployment configuration
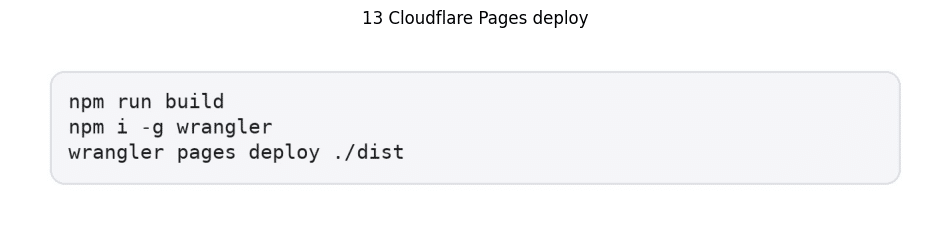
Cloudflare Pages deployment requires technical expertise:
- Build process execution with npm run build
- Wrangler installation through npm i -g wrangler
- Deployment configuration via wrangler pages deploy ./dist
Monitor performance and errors
Post-deployment monitoring demands sophisticated tooling and analysis:
- Complex analytics implementation for user behavior tracking
- Error logging system configuration
- Performance metric monitoring setup
While platforms like Vercel offer preview deployments for pull requests, maximizing these features requires deep technical understanding. Self-hosted solutions demand even more extensive configuration expertise.
Pre-commit hook implementation requires careful setup:
This critical protection layer demands proper configuration to effectively prevent production issues.
Plan for future upgrades
Maintaining a React application long-term requires intricate planning and specialized expertise. Consider these critical practices:
Implementing automation post-migration demands technical proficiency. While GitHub integration with hosting platforms enables automatic deployments, configuring these CI/CD pipelines requires deep understanding of deployment workflows.
Custom domain configuration, though available on platforms like Vercel and Netlify, involves complex DNS management and SSL certificate setup.
VS Code configuration requires careful consideration:

This intricate setup demands expertise to optimize development workflows.
Maintaining GitHub synchronization with development workflows requires sophisticated version control knowledge and careful environment management.
Need to export Lovable.dev to React?
We help founders migrate Lovable.dev projects into production-ready React/Next.js apps. Want a quick review of your export and the fastest path to launch?
Contact UsTransitioning from Lovable.dev to React represents a complex technical challenge requiring specialized expertise. The migration process involves intricate steps that demand thorough understanding of both platforms.
While the export package provides a Vite-based React application, properly configuring and maintaining it requires deep technical knowledge. GitHub integration and manual exports each present their own complexities that need careful consideration.
Environment variables, dependency management, and helper code migration involve sophisticated troubleshooting skills. Setting up a proper React development environment demands extensive configuration expertise.
AI development tools like Cursor, Windsurf, or Claude require proper integration and usage knowledge to maximize their potential.
Existing codebase maintenance demands careful planning and technical proficiency. Successfully managing incremental improvements requires deep understanding of React architecture.
Deployment platforms offer various features, but configuring them optimally needs specialized knowledge. Application success depends on complex technical decisions around workflows, domains, and monitoring.
React’s advanced features like server-side rendering and deployment flexibility come with significant implementation challenges. The migration requires extensive technical expertise—making it crucial to engage experienced developers who understand these complexities.
Post-deployment maintenance involves sophisticated performance optimization and strategic planning. This migration represents a technically demanding process that requires professional expertise to ensure long-term success and scalability.
FAQsQ1. How can I export my Lovable.dev project to React? You can export your Lovable.dev project to React using either GitHub integration or manual ZIP download. GitHub integration allows for continuous synchronization, while manual download provides a quick snapshot of your project files.
Q2. What should I do after exporting my Lovable project to React? After exporting, set up your local React environment by installing dependencies, configuring environment variables, and verifying that all user flows work correctly. Address any missing environment variables or dependency conflicts, and preserve helper code to ensure functionality.
Q3. Is it necessary to completely rewrite my exported Lovable code in React? No, it’s not necessary or recommended to completely rewrite working code. Instead, focus on gradual improvements and feature delivery. Use the “Strangler Pattern” to incrementally replace parts of your application while maintaining functionality.
Q4. How can I speed up development after migrating to React? Integrate AI coding agents like Cursor, Claude, or Windsurf to streamline development. These tools can help with debugging, feature building, and refactoring. Provide proper context to the AI and use it for both exploring approaches and implementing changes.
Q5. What are the best options for deploying my React app after migration? Popular deployment options include Vercel, Netlify, and Cloudflare Pages. These platforms offer easy setup, custom domain support, and integrated monitoring tools. Choose based on your specific needs for performance, ease of use, and additional features like form handling or A/B testing capabilities.

- What You Get When Exporting from Lovable.dev
- Checklist before exporting
- Choose Your Export Method: GitHub vs Manual
- Step-by-Step: GitHub Export Configuration
- Post-Export Technical Considerations
- Set Up Your React Environment
- Integrate AI Coding Agents for Faster Development
- Avoid the Rewrite Trap
- Deploy and Maintain Your React App
- Conclusion
- FAQs



